
Why would someone use Dursan® in their HPLC column and equipment flow paths? Let's discuss the benefits of using a CVD coated flow path for solving HPLC test problems.
PEEK, stainless steel, and titanium all are used in high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) flow paths, either in sample transfer, filtration or in the column themselves. All are good materials but they can have limitations.
- PEEK- Very inert polymer, works for low pressure, but under high pressure the tubing can rupture. PEEK frits can deform under high differential pressure.
- Stainless steel- Robust but reactive surface. Stainless can adsorb reactive analytes resulting in peak distortion, lost peaks or failed tests.
- Titanium- Bio-inert in nature, can have reactive sites, plus titanium is expensive.
Surface reactivity and material durability can hamper HPLC test performance and reliability.
- Analytes can be lost
- Peaks can be broad
- Testing can be unreliable
- Lost peaks
- Equipment failures
|
In this blog post you will learn:
How Dursan® coated surfaces can improve HPLC test results
- The limitations of materials commonly used in HPLC systems.
- The benefits of using high purity CVD coatings for chelating agents, protein and organic molecule separations.
- How precision coatings impact column packing efficiency.
|
 What benefit does Dursan® offer over other materials for inertness?
What benefit does Dursan® offer over other materials for inertness?
Dursan coated stainless steel flow paths and columns can dramatically improve the inertness of stainless steel while maintaining a robust system at a cost that's significantly cheaper then titanium. Dursan® is a thin flexible CVD coating that can penetrate and line all areas of the HPLC flow path including:
- Fritted filters
- Needles
- Stainless steel tubing
- Fittings
- Columns
- Valves
Because Dursan is inert, the coating won't negatively impact the performance of test molecules and will improve the performance of compounds like:
- Chelating agents
- Proteins
- Organic molecules
Let's discuss comparative test results and learn more about the performance of CVD coated flow paths in HPLC applications. For more information about our metal free performance coating technology get our presentation or watch our webinar.

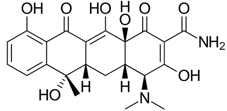
Chelating agents like tetracycline
- Tetracycline is an antibiotic, commonly used for acne and skin infections
- The molecule has numerous chelating groups that bind readily to metal sites
- Dursan can make the steel column more inert toward metal loving molecules like tetracycline
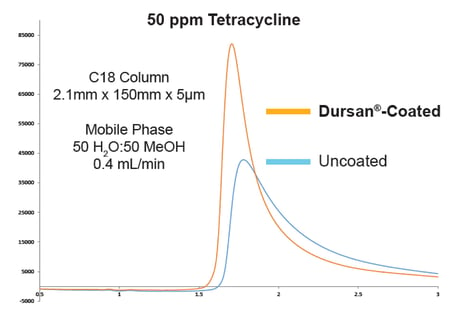
The comparative chromatograph below tells the story. The resolution quality of tetracycline on a stainless steel column showed poor peak shape and response. The Dursan® coated column significantly improved the peak shape and significantly improved response.
Dursan prevents chelating groups from binding to metal sites. This can be a significant issue for high surface area components like sintered metal frits. Let's compare the peak shape performance of coated and uncoated frits and columns for chelating applications.
Parameters for the test were:
- Mobile Phase A: Water
- Mobile Phase B: Methanol
- 40% B
- Flow: 0.3mL/min
- Detection: 265nm
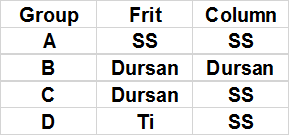
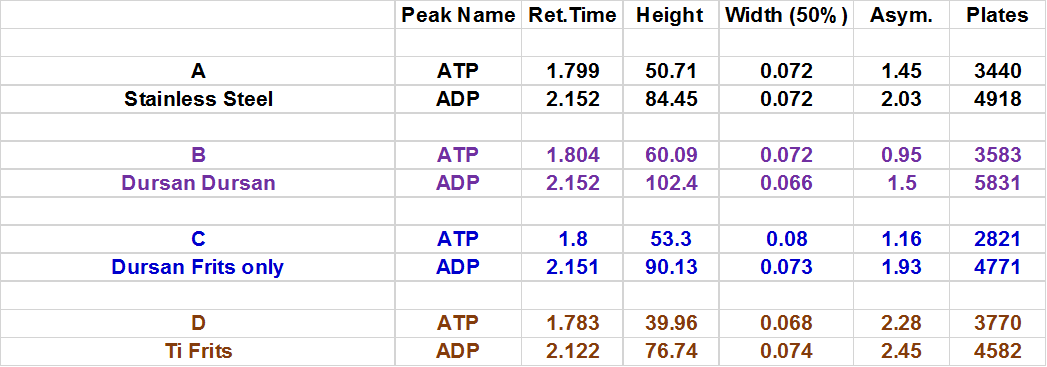
We injected the solution onto several coated and uncoated columns to compare peaks and overall performance. Materials were grouped into 4 tests, A, B, C, and D outlined below.
The Dursan® coated surfaces improved peak resolution and peak shape significantly as compared below.
|

Group A: SS Frit & Column
|

B: Dursan Frit & Column
|

C: Dursan Frit, SS Column
|

D: TI Frit, SS Column
|

Proteins
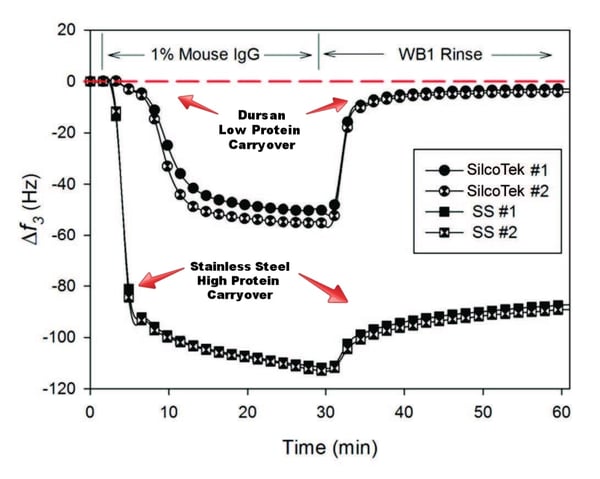
Comparative studies with Abbott Laboratories demonstrated the non stick feature of Dursan. Through our collaborative study with Abbott Laboratories, Dursan was shown to prevent non-specific protein binding and minimize protein fouling. Studies highlighting separations on HPLC peptide standard mixture, ribonuclease, cytochrome C, bovine serum albumin, and proteins show better response and minimum retention of the analyte on the surface, preventing cross contamination.
QCM-D analysis of coated and uncoated stainless steel surfaces show significant increase in protein mass on the stainless steel surface. The Dursan coated surface does not retain proteins, showing no increase in mass after washing with a non-ionic surfactant. This demonstrates the non stick feature of the coating.
Want to learn more about our protein study? Read the complete whitepaper.

Organic Molecules
Organic molecules like phosphates can perform poorly in stainless steel flow paths. We compared the performance of phosphate interaction in stainless and Dursan coated systems. Results show a significant improvement in performance.
- Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) provides energy to drive numerous processes in living cells
- It is typically converted to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
- Phosphates are well known to have severe peak tailing during HPLC analysis due to the phosphate-iron interaction
Packing Efficiency
Does the application of Dursan® to columns and frits have an effect on packing efficiency or flow? We compared coated and uncoated columns and found comparable packing efficiency.
|
Column type
|
Efficiency (avg of 3)
|
Asym (avg) of 3
|
|
Stainless Steel
|
15195 plates
|
1.028
|
|
Dursan coated frit and column
|
15233 plates
|
1.026
|
|
With Dursan coated frit, SS column
|
15069 plates
|
1.020
|
|
Titanium frit SS column
|
14263 plates
|
1.044
|
Comparison of plates show there are negligible effects on pressure and column packability. Why is packability not effected by the coating? Because the coating process results in a micron thick surface on larger geometries like columns. And on fine geometries, like frits, the coating process results in a 100 nm thick surface. The super thin but durable coating has a minimal impact on overall volume and efficiency.
In a previous blog post we discussed the question: Is Dursan resistant to TFA in HPLC testing applications. Read that post here to learn more about how the coating performs.
Get more information on how our coatings perform in HPLC applications.
Ask the experts.

Our Technical Service Team is here to help you select the best coating for your application.
Our team can:
Want more in-depth information about our coatings and learn how they improve the performance of products and processes in challenging applications?

 What benefit does Dursan® offer over other materials for inertness?
What benefit does Dursan® offer over other materials for inertness?












