
Prevention of non-specific protein adsorption is highly desirable in many fields including food, marine and medical industries. Biofouling or protein adsorption can be a significant issue in medical sampling systems, causing false positive readings due to protein carryover. No one wants to be told they have a serious illness when in fact the test system recorded a false positive due to protein carryover.
|

|
There are a limited number of materials that are effective in preventing protein adsorption (non-specific protein binding), even fewer can withstand the abrasion and exposure to corrosive cleaners associated with biomedical autosampling systems. |
Fortunately biofouling in biotech applications can be prevented by following these 3 precautionary measures:
- Pre-exposure: prevent non-specific adsorption by modifying the surface chemistry with a bioinert coating.
- During-exposure: change the solution properties (such as pH, ionic strength) by using excipients such as ionic or non-ionic surfactants to alter electrostatic as well as hydrophobic interactions.
- Post-exposure: use wash/rinse solutions containing caustic chemicals.
These measures on its own cannot provide a universal fix to the biofouling problem, but various combinations of these three are effective in preventing biofouling and protein carryover.
Bioinert Dursan® Helps to Reduce Carryover
Combining robust bioinert Dursan® coating and a non-ionic surfactant in the wash buffer is an example of a step forward in preventing biofouling; specifically in the case of automated assay analyzers, reagent manufacturing, and filling setups. Dursan significantly reduces carryover compared to conventional PEG coatings.
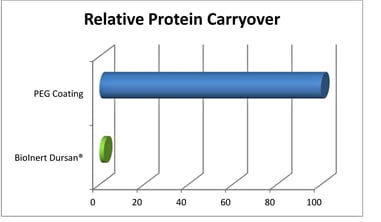
Dursan coating is physically more robust than liquid-based coatings or PEEK while being naturally inert.
 Dursan's hydrophobic, low surface energy resists sticking of proteins from tissues, blood and other media.
Dursan's hydrophobic, low surface energy resists sticking of proteins from tissues, blood and other media.
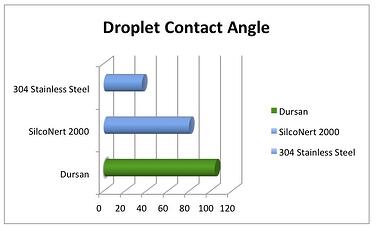
Dursan® is a layer of elemental silicon, oxygen, and carbon that binds molecularly to the base substrate of glass, ceramics, stainless steels and other alloys. Applied via chemical vapor deposition (CVD), the coating is extremely thin - less than 2µm - and will penetrate even the smallest holes and most complex geometries.
Treat the entire analytical flowpath
Dursan® is a common treatment for a variety of bio-analytical componentry like:
- Needles and probes
- Biosensors
- Diagnostic equipment flow paths
- Auto sampling systems
- Biomedical devices
- Biosensors
- Tissue engineering components
- Liquid chromatography
|
 |




 Dursan's
Dursan's


