In this blog post we discuss key factors to consider when selecting a coating for bioinert test applications in medical diagnostics and HPLC.
Stainless steel, a common medical diagnostic flow path material, is an active surface that can cause protein retention, chemical adsorption and is susceptible to corrosion when bleach or acids are used as a cleaning or rinse agent. That’s why various types of coatings have been used to improve the surface properties of medical diagnostic instruments and HPLC instruments for decades, but none have been completely successful in reducing protein retention and carryover.
|
In this blog post you will learn:
- Factors to consider when selecting materials for bioinert test applications
- About FDA compliance and Dursan
- How instrumentation benefits from a bioinert surface
- Why Dursan is the ideal coating for HPLC and medical diagnostics applications
|
Instrument manufacturers have gone to great lengths to evaluate alternative materials to solve non-specific protein binding, protein carryover, fouling and rust problems. Unfortunately, commonly used fluoroploymers, like AF1600, are not acceptable in high durability applications. Small bore surfaces like needles, valves, or fittings are also challenging for polymer-based or other line-of-sight coatings. To address durability and form factor concerns, manufacturers take into account several key factors when selecting bioinert materials.
Factors to consider when selecting bioinert materials:
- Improved analytical sensitivity, eliminating interaction with flow path surfaces.
- Prevent non-specific protein binding for proteins. This avoids carryover and false positive results.
- Corrosion resistant and durable.
- Able to be applied to surfaces without changing part tolerance or performance.
- Meets FDA regulatory compliance for coatings.
Go to our Medical Device and Diagnostic Applications page to learn how coating specific flow path components can improve the performance of medical diagnostic and HPLC instrumentation.

About NSF approval and FDA Compliance
When a coating, like Dursan®, is compliant with NSF/ANSI 51 and all applicable requirements. That means that it is safe for food contact and also meets the FDA’s requirements for compliance. FDA regulates coatings via the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), specifically 21 CFR 175.300 which lists what raw materials are acceptable and unacceptable for the formulation of coatings. According to the FDA, a coating must:
- Pass the solvent extraction tests listed in 21 CFR 175.300.
- Contain no heavy metals.
- All coating components must conform to the materials listed by the FDA in order to be compliant.
These stipulations are also required for NSF/ANSI 51 certification. Dursan® successfully meets these NSF requirements and consequently is FDA compliant.
Click here to view our NSF certificate
Why are inert CVD coatings an ideal solution to common bioseparation problems?
An inert sampling flow path is critical for achieving consistent bioseparation in medical diagnostics and HPLC analysis. Over time inert surfaces degrade and test flow paths corrode due to frequent rinse cycles from aggressive chemicals like bleach. The corroded and pitted surfaces are perfect hiding places for sticky compounds like proteins, making carryover and contamination a real concern. Inert CVD coatings like Dursan® solve these problems and improve versatility and performance of the analytical flow path.
Coating properties that will improve instrument flow paths include:
Anti-stick
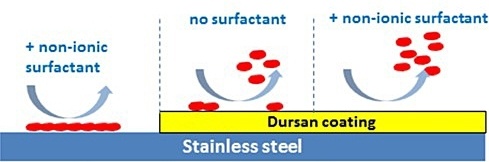
Proteins can stick to stainless steel surfaces and hide in corroded surfaces. Rinsing can remove most but not all the analyte from the surface (left image below). The Dursan coated surface reduces stiction so all the analyte is removed from the surface when rinsed with a non-ionic surfactant. This prevents carryover and contamination of future test samples.
Non-reactive/inert
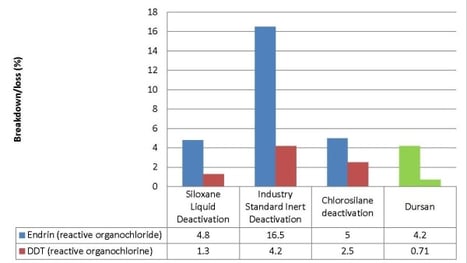
Stainless steel is reactive so it's a smart idea to apply a deactivation solution to the flow path surface. This prevents loss of analyte or breakdown of test chemicals. Unfortunately many deactivation solutions lack the durability and inertness to effectively prevent activity over repeated injections or tests. Breakdown loss comparisons show Dursan is an effective deactivation and offers high durability, temperature resistance, corrosion resistance and improved simulated distillation and sulfur analysis.
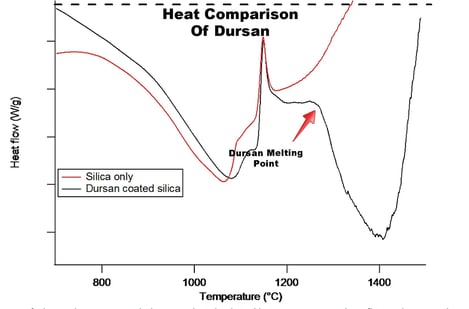
High temperature resistance
Many deactivations and coatings will fail at temperatures above 350c. Silicon CVD coatings like Dursan remain completely inert and stable up to 450c and won't fail when exposed to temperatures above 1000c (however, some loss of inertness, durability, and corrosion resistance may occur).
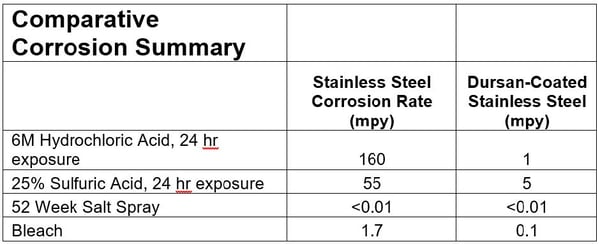
Corrosion resistance
Exposure to corrosives like bleach and chlorides can pit flow path surfaces (where proteins can hide) and can cause rust particulate contamination. Stainless steel corrosion can be reduced by an order of magnitude by applying Dursan to the exposed surfaces.
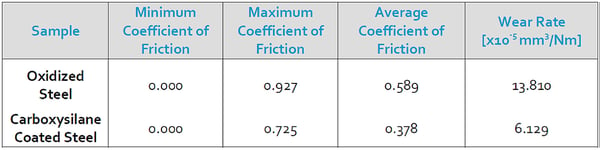
Wear & Abrasion Resistance
Pin-on-disc wear measurements show silicon carboxysilane coated steel (Dursan) can reduce wear rate by 50% compared to uncoated stainless steel. Improved wear resistance can increase needle life, allowing more injections before maintenance and longer component life.

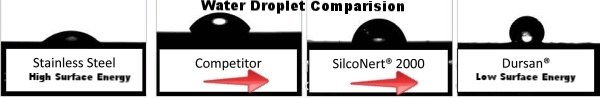
Hydrophobicity
Trace moisture can adsorb and react with the sample and cause test failures. That's why managing moisture is a key factor in optimizing bioinertness. Moisture can also contribute to corrosion which can damage flow path surfaces. Dursan repels water as seen in the comparative water droplet test below. Uncoated stainless steel wets the surface, allowing trace moisture to accumulate in the test system. The Dursan coated surface repels the water drop, creating a hydrophobic surface that prevents wetting and potential contamination and corrosion.
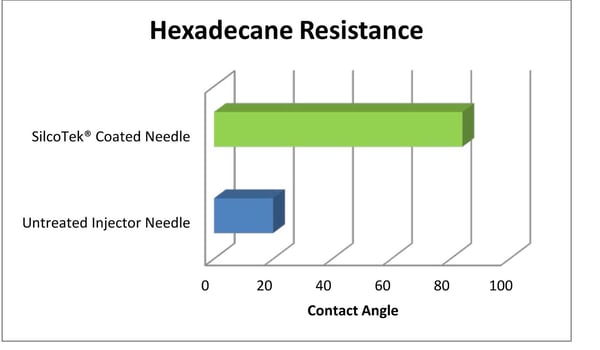
Oleophobicity
Oil and gas as well as some HPLC applications require an oil repelling surface. Oil will wet and stick to a stainless steel surface, causing cross contamination. The Dursan coated surface (below) repels oil and distillates, minimizing wetting of the surface.
How do coatings benefit medical diagnostic and bioseparation components?
Bioinert Dursan® prevents interaction of reactive, corrosive, or sticky compounds in analytical flow paths. Benefits include:
- Extend the life of needles and flow path components
- Prevent protein carryover and binding
- Improve test consistency
- Prevent false positive results
- Improve Simulated Distillation and Sulfur Analysis
If you want to learn more about our coatings and how they improve flow path performance:
Download our Coatings Guide










