The second book in our four part Analytical e-book series is entitled, An Introduction to Inert Coatings. It takes you through our process, the benefits the coating provides, and data to help you choose the right coating for your application. This e-book goes into more detail than this blog post, so be sure to check it out.
In case you missed it, here's a link to the blog post for the first book in this series.

What are Inert Coatings?
Inert coatings are non-reactive barrier materials that are bonded to a flow path container (be it tubing, sample cylinder, instrument components or other structure). Inert coatings offer known benefits to applications ranging from process analytical, chemical process, & refinery, to semiconductor manufacturing.
Chemical vapor deposition coating process
SilcoTek’s CVD coating process starts with a thorough assessment of the parts and customer requirements. Understanding the customer performance need, specifications, and end use help to assure that the best coating for the application is applied.
Watch our coating process video to learn more!
How does an inert coating improve my process or product?
Inert coatings offer three distinct properties that improve process analytical systems:
Corrosion resistance
SilcoTek® coatings resist corrosive attack by acids commonly used in chemical process, refinery and analytical applications. SilcoTek coatings can extend the life of tools by 10x or more. Comparative results show inert coatings like Dursan can significantly improve corrosion resistance over stainless steel and other steel alloys. Dursan performance compares favorably to super alloys. HCl immersion tests show uncoated stainless steel severely corrodes, turning the acid green. The Dursan coated coupon shows minimal corrosion and uncontaminated acid.

Purity
SilcoTek coatings act as a barrier, preventing contact of the test analyte with reactive stainless steel or glass substrate. A high purity surface prevents contamination of the process fluid and prevents bonding of “sticky” media to the surface. The high purity silicon surface won’t allow corrosive gases from leaching metals from the surface, improving process yield and analytical test accuracy.
Inertness
Inert coatings do not adsorb or react with product or sample flow, preventing test failures, inaccurate results and contamination. An inert surface will improve system response because there is no interaction with the test sample.
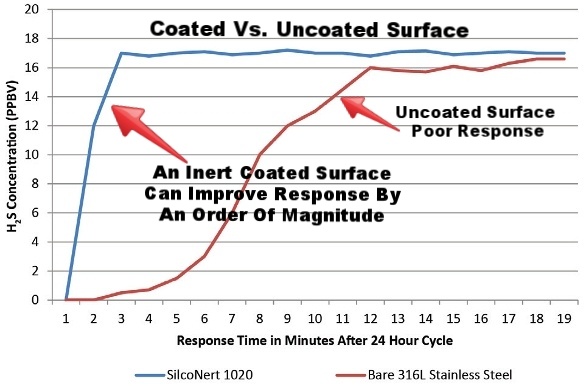
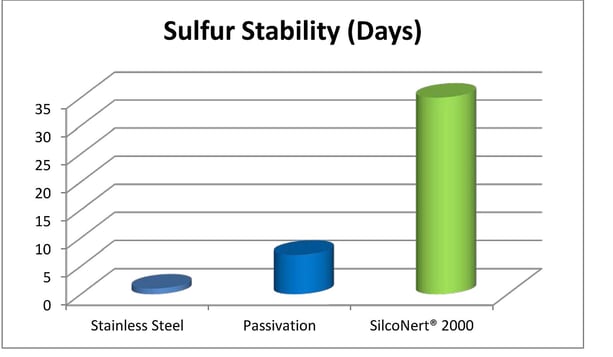
Inert Coatings, not Passivation: the Answer for Accurate Sulfur Test
Inert coatings offer significant benefits over traditional surface passivation or priming techniques used in analytical and sample transfer systems. Industry white papers and articles have proven that surface interaction and corruption of sample results can be avoided through the use of inert barrier coatings. Reactive or active compounds found in hydrocarbon processing and environmental sampling can be especially difficult to accurately test at low part-per-million or parts-per-billion sensitivity. That’s why a non-reactive flow path has become the industry standard for a high performance sampling system.
Benefits include:
- Accurate and reliable H2S & sulfur test data
- No delay in analyzer response
- Reduced sample error & false readings
- Improved product yield and test productivity
- Faster cycle times
Passivation Not the Answer
Passivation or priming is a technique that is based on the assumption that if all active sites of a transport system or storage vessel are taken up by a reactive analyte, like sulfur compounds, those active sites are “filled” and can no longer take up sulfur compounds or other reactive compounds. Early studies supported this idea for low temperature gas phase transport of relatively high concentration sulfur compounds through low surface area components.
An Alternative for Corrosion Resistance and Inertness

Corrosion can not only compromise analytical system integrity and increase maintenance cost; it can also generate particulates that can result in obstruction and fouling of the system and cause adsorption of reactive compounds, ultimately compromising test results. Pitting can also create excellent hiding places for “sticky” molecules, resulting in carryover and false positive results. Passivation and polymeric coatings have been utilized to reduce corrosive attack, but there’s a higher performing alternative that improves both inertness and corrosion resistance of the surface.
About Passivation
Nitric acid passivation is commonly used in an effort to remove exogenous iron from surfaces and to prevent staining in the hope that the stainless steel flow path will become more corrosion resistant or inert.
Unfortunately, when applications require the use of aggressive agents like bleach, sulfuric, or hydrochloric acid, no amount of passivation or electropolishing will prevent corrosive attack.
An Alternative to Passivation
There is an alternative to passivation that produces better results: change the surface properties of the material by bonding enhanced silicon compounds onto the steel surface via chemical vapor deposition (CVD). A coating like Dursan®, for example, will improve the corrosion resistance and inertness of the surface, offering a multitude of benefits. The chemical vapor deposition process used to passivate stainless steel flow paths will prevent disruption of grain boundaries and act as an inert barrier to aggressive and sticky compounds. Dursan-coated analytical flow paths will prevent HCl, sulfuric acid, bleach, and other corrosives from pitting and attacking stainless steel surfaces.
The Dursan® Process

The Dursan CVD coating process is quite different than typical surface treatment or coating methods, even compared to other CVD methods. In addition to the coating deposition itself, the Dursan process also contains the following steps:
- Surface preparation (typically aqueous sonication)
- Multi-step deposition of silicon and other compounds to the surface
- Post-deposition cleaning
- Testing and inspection
Protecting Stainless Steel from Corrosive Attack in Continuous Emissions Monitoring (CEMS) Flow Paths
Dursan can increase corrosion resistance by 10x or more through preventing interaction of the analyte or process fluid and the stainless steel surface. Dursan exceeds typical metal passivation capability and inertness by orders of magnitude while maintaining dimensional tolerance. Immersion testing in 6M hydrochloric acid (HCl) shows that Dursan coated surfaces prevent surface attack by orders of magnitude compared to passivated stainless steel.
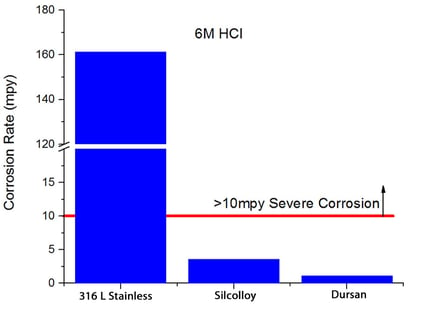
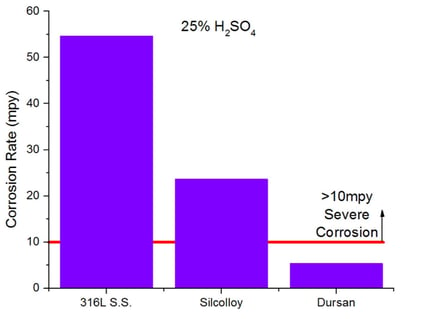
Stop Carryover and Contamination
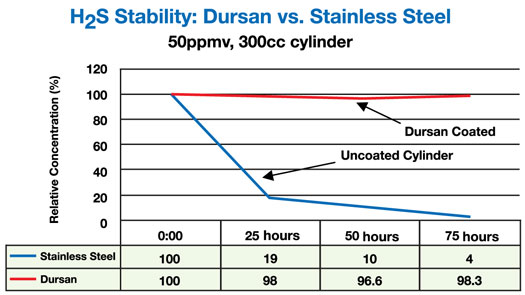
Sticky compounds like COS and H2S can be difficult to remove from CEMS sampling flow paths. Existing techniques for enhancing release such as priming do not assure complete inertness of the analytical flow path. SilcoTek provides an alternative coating solution in Dursan that offers better stability in air and other oxidative environments, even under elevated (450° C+) temperatures. Dursan ensures near-zero adsorption compared to passivated stainless steel.
Choosing the Right Coating
SilcoTek’s technical experts are here to help you select the best coating for your application. Some applications may require specialized treatment, but often one of our standard surface coatings will perform well for you. SilcoTek’s complete platform of coating solutions offers a multitude of surface properties for your most challenging applications:
- Low surface energy
- Oleophobicity
- Hydrophobicity
- Abrasion resistance
- Easy cleaning/anti-stick
- Chemical inertness/compatibility
- Corrosion resistance
- Anti-coking/anti-fouling
- High purity/low outgassing
- Contamination resistance
Common Applications
SilcoTek offers a range of coatings developed to solve difficult material problems in a wide variety of industry, analytical, process, and research applications. Our technical staff can also modify an existing coating or develop a new coating technology to meet your needs.Common coating applications include:
- Refinery, flare, and flue gas
- LNG/CNG sampling and testing
- Process monitoring
- Air emissions analysis
- Chemical manufacturing
- Power generation (coal-fired)
- Odorant sampling
- Moisture analyzers
- Liquid and gas chromatography
- HCl streams
- NOX and SOX
- Mercury
- Ammonia
- Low sulfur regulation compliance
- Research (reactors, vacuum, etc.)
- Hydrocarbon analysis
Tips for Selecting the Right Coating
A successful coating solution involves matching the performance environment of both the application and the coating. Here are questions to consider and review with SilcoTek’s technical experts before making a coating selection.
Chemical exposure and environment
- Is the application exposed to acids or bases?
- What target chemicals are you sampling?
- Duration of exposure
- Operating temperature
- Cleaning solvents and methods used
- Abrasives or other durability concerns
- Previous chemical exposure of the part
Form factor of the part
- What areas of the part are sensitive to damage?
- Surface finish of the part
- Wear points of the part
- Metallurgy of the part
- Where can the part be held with a handling fixture?
- Are there seals or o-rings in the part?
- Is the part disassembled?
Performance requirement of the part’s surface
- How do you need the surface to behave? Corrosion resistant, inert, hydrophobic, etc.
- Are there welded or brazed/soldered joints in the component?
- Are there blind holes or small cavities in the part?
- Overall dimensions and quantity
Conclusion
So, what have we learned about inert coatings? Silicon coatings applied by chemical vapor deposition have several advantages over polymer coatings and even super alloys:
- Chemically compatible, inert, non-reactive
- Boost analytical performance by preventing adsorption. Excellent in several applications, including:
- Sulfur analysis/sampling
- Environmental analysis
- Chromatography
- Stack and flare sampling
- Downhole oil and gas sampling
- Improve corrosion resistance
- Increase purity
- Increase durability















