People use barrier coatings to improve the performance of their products. For example, coatings can improve corrosion resistance, make surfaces inert, reduce product contamination, or for improve non-stick performance. But what about coating pitfalls?
Barrier Coating Benefits and Pitfalls
Coatings are used to economically improve the performance of the base material, product or process. Using the right coating for the right application is key to avoiding coating problems. In this blog we discuss coating benefits and pitfalls.
|
In this blog post you will learn:
- Key benefits and takeaways from using barrier coatings in a variety of applications.
- We'll discuss some potential pitfalls relating to the use of barrier coatings and how to avoid future coating performance problems.
- How to pick the right CVD coating for your application
|
CVD Coating Benefits
Not all coatings work for all applications. For example an acrylic coating may be an economical corrosion fighter in some applications, but try and use that coating in an abrasive environment or in an application where a non reactive surface is needed and the results will be disappointing. In the examples below we'll discuss the benefits of silicon coatings applied by chemical vapor deposition. Polymeric coatings or metallic coatings will perform differently, so be sure to evaluate the coating in the application before use.
Corrosion resistance
Barrier coatings protect critical surfaces from corrosion and contamination, improving component durability and process yield. Benefits include:
- Improved corrosion resistance
- Less metal ion contamination
- Outstanding moisture control

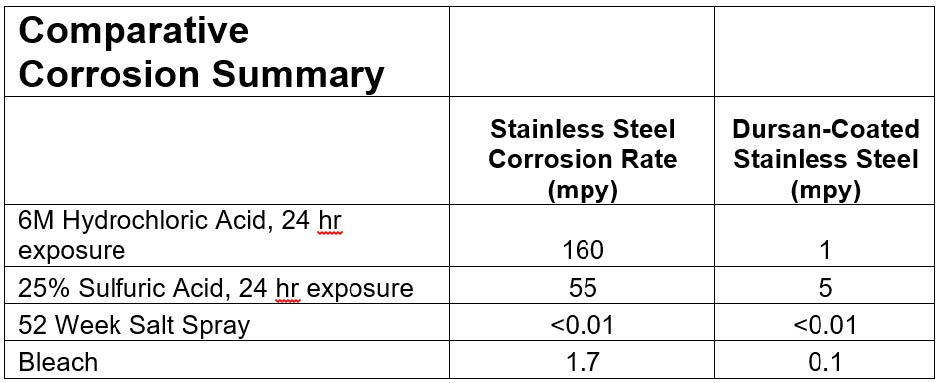
The comparison below highlights the improved corrosion performance of CVD barrier coatings. Coated surfaces offer a 10x or greater improvement in corrosion resistance without changing the product material or design.
Inertness

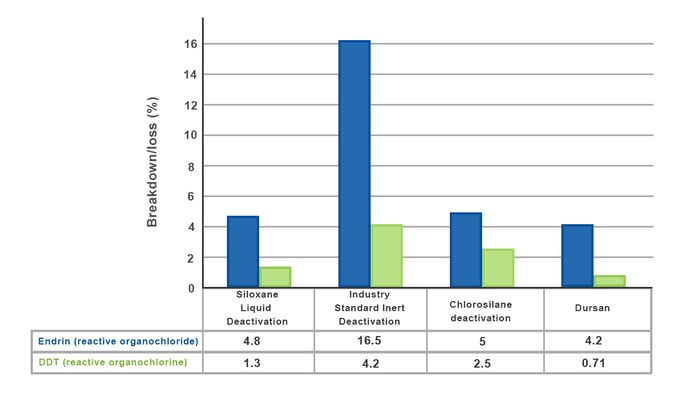
Coatings, like SilcoNert® improve lab and instrument performance by creating a chemically inert flow path which prevents sample adsorption and reactivity. Benefits include: fast response, improved sensitivity, low distortion, reduced carryover and contamination. Comparative testing (below) of reactive organochloride and organochlorine show significant improvement of inertness over polymeric coating deactivation.
Hydrophobicity

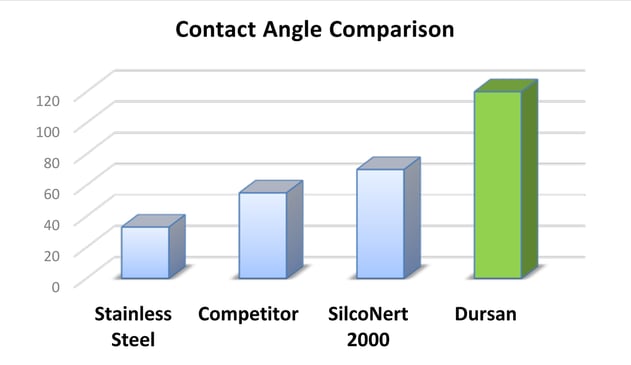
SilcoTek's inert high temperature barrier coatings enhance hydrophobic performance of critical flow path surfaces. Dursan® coating improves moisture repelling properties of stainless steel, glass, and ceramic surfaces by 60% or more, minimizing wetted surface effects.

Water droplet contact angle measurement (below) shows a significant improvement in water repelling properties. Coatings that repel water can improve corrosion resistance and help manage moisture in processes sensitive to water contamination.
Non-stick fouling resistance and mold release
Low surface energy silicon CVD coatings reduce surface friction and stiction, and improve carbon coking and fouling resistance. Coatings can help improve engine efficiency, reduce maintenance and improve plastic mold release and durability. Fouling tests (below) show significant improvement in carbon coking resistance when using silicon coatings.
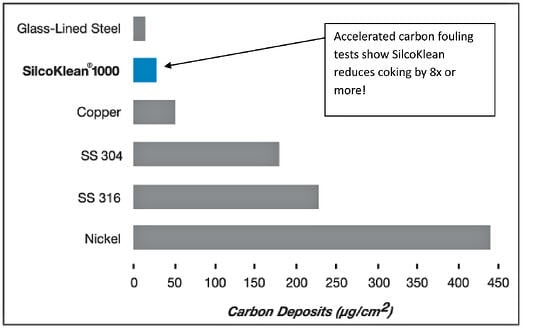
Barrier Coating Pitfalls
Barrier coatings offer many benefits but can also present some significant challenges. Poor coating selection, improper surface preparation, or substrate compatibility issues can lead to coating failures and performance issues. Let's discuss some common coating pitfalls.
Pinholes or coating breaches
Pinholes or small point source channels can result from surface contamination during the coating process or as a result of outgassing when applying a coating. Channels or breaches can act as a conduit for cathodic reactions which can result in concentrated corrosive attack at the pinhole. Coatings that are electrically conductive and support cathodic reactions, oxygen reductions or hydrogen evolution are more likely to promote a cathodic reaction and localized corrosion. Avoid conductive polymers and noble metals (ie. copper, silver, gold) as a barrier coating for corrosion applications when protecting more active metals like aluminum or steel.
Barrier coatings that are are not conductive or less conductive provide better cathodic protection and will reduce the potential of corrosive attack at voids, pinholes or breaches. Proper surface preparation can also help to prevent pinholes. The EIS corrosion resistance test below demonstrates how a properly applied coating can significantly improve corrosion resistance and minimize pinholes. The CVD coated sample (blue lines below) show minimal current breakthrough, indicating minimal pinholes in the coating surface.
/Pinhole%20and%20Silcolloy.png?width=587&name=Pinhole%20and%20Silcolloy.png)
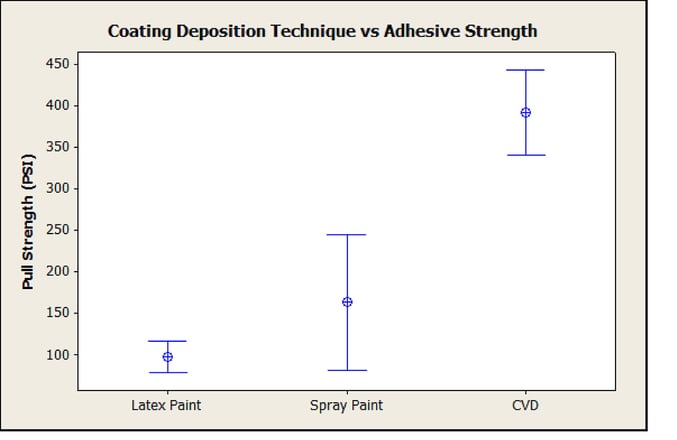
Coating adhesion problems
Surface contamination can result in poor bonding of a coating to the surface. That can lead to adhesion problems and failure of the coating. The coating comparison below shows how adhesion can vary significantly between coatings. Paints can have significant adhesion issues because preparation of the underlying surface can vary. Salts, particulates, grease of other contaminants can significantly impact adhesion.
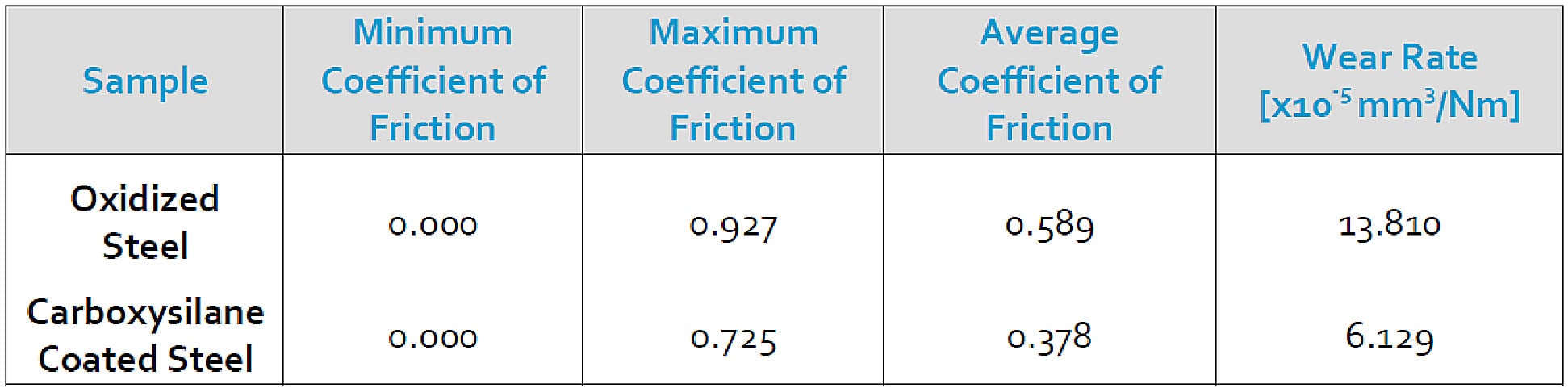
Abrasion/wear
Polymeric and softer metals can lack abrasion and wear resistance. In industrial applications this can lead to a loss of coating at the wear site. Pin on disc wear testing, surface impact testing, or bend/stress testing can determine if the coating is appropriate for your application. Compare coated samples to the base metal performance. In the example below, an pin on disc test compared oxidized stainless steel to carboxysilane (Dursan) coated stainless steel. In this test, the coating proved beneficial in the application and showed significant reduction in friction and wear rate.
Moisture interaction
Brush on or spray on coatings (i.e. organic coatings like epoxies, paints, acrylics) have some degree of water permeability. They can absorb moisture and can be problematic in high humidity environments. If the coating to surface interface is robust, that absorbed moisture won't lead to a corrosion problem but if the surface interface is poor (due to surface contamination), moisture can build up at the coating-substrate interface and cause blisters and coating failure.

Coating cracking
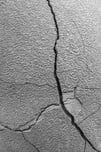
Oxide, nitride and carbide coatings are resistant to moisture but can lack the flexibility needed to remain intact under stress. These coatings can crack or delaminate from the surface under extreme conditions. Flex testing and impact testing help quantify how the coating will perform in the application.
Learn more about potential coating pitfalls by going to our Frequently Asked Questions page. You'll come away with lots of CVD coating information.
CVD Coating Frequently Asked Questions
How SilcoTek coatings stack up?
Pinholes
 Silcotek® coatings minimize pinhole effects through improved surface preparation techniques and rigorous process controls. Silcotek's silicon CVD coatings demonstrate electrically neutral to insulative characteristics which minimize cathodic reactions in the event of a coating breach.
Silcotek® coatings minimize pinhole effects through improved surface preparation techniques and rigorous process controls. Silcotek's silicon CVD coatings demonstrate electrically neutral to insulative characteristics which minimize cathodic reactions in the event of a coating breach.
Adhesion
 SilcoTek's proprietary surface preparation methods and rigorous process controls help to improve the quality of the bond between the coating and substrate. This dramatically improves adhesion compared with other coatings.
SilcoTek's proprietary surface preparation methods and rigorous process controls help to improve the quality of the bond between the coating and substrate. This dramatically improves adhesion compared with other coatings.
Abrasion/wear
 Wear resistance testing shows SilcoTek coatings, like Dursan, show improved wear resistance compared to polymeric coatings.
Wear resistance testing shows SilcoTek coatings, like Dursan, show improved wear resistance compared to polymeric coatings.
Moisture resistance
 Coatings like Dursan and Notak repel water. This improves corrosion resistance and moisture management in systems sensitive to moisture contamination.
Coatings like Dursan and Notak repel water. This improves corrosion resistance and moisture management in systems sensitive to moisture contamination.
Selecting the Right Coating
Coating performance is one factor in a successful coating outcome but the most important factor is selecting the right coating for the application. There are a vast number of coatings available so it's wise to research the coating before using it in your application.
Tips for Selecting the Right Coating

A successful coating solution involves matching the performance environment of both the application and the coating. Here are questions to consider and review with SilcoTek’s technical experts before making a coating selection.
1. Chemical exposure and environment
- Is the application exposed to acids or bases?
- What target chemicals are you sampling?
- Duration of exposure
- Operating temperature
- Cleaning solvents and methods used
- Abrasives or other durability concerns
- Previous chemical exposure of the part
Why is this important?
Because chemical exposure can be a source of pitting and surface damage that can lead to chemical adsorption and sample or product cross contamination. Protecting the surface by applying a high durability, inert coating can improve performance but exposure can play a big part in overall life of the coating. Sometimes we'll select a slightly less inert but more durable coating in order to strike a balance between performance, durability and coating life.
2. Form factor of the part
- What areas of the part are sensitive to damage?
- Surface finish of the part
- Wear points of the part
- Metallurgy of the part
- Where can the part be held with a handling fixture?
- Are there seals or o-rings in the part?
- Is the part disassembled?
Why is this important?
Because part metallurgy and surface finish can play a role in coating compatibility and adhesion. We can apply coatings to most metals but there are some (like copper and copper alloys) that react negatively to silicon surface bonding. This can result in poor coating morphology and reactivity. Wear or damage sensitivity can dictate handling and coating selection. We may fixture a part differently depending on the surface and we may select a more durable coating in wear applications. O-rings and part assembly can severely impact coating quality, so we request the part be completely disassembled to assure quality.
3. Performance requirement of the part’s surface
- How do you need the surface to perform? Corrosion resistance, inertness, hydrophobic, etc.
- Are there welded or brazed/soldered joints in the component?
- Are there blind holes or small cavities in the part?
- Overall dimensions and quantity

Why is this important?
Desired performance is obvious. We don't want to apply a coating that does not meet performance expectations, but we also want to know about the overall part configuration, it's precision and if there are small flow paths. That's because we often specify special preparation, fixturing or processing for intricate or high precision parts.
That’s a lot to consider! If you don’t know something about a part, our technical staff and production technicians will address any questions or potential issues. If you know lots about your part, you may feel comfortable selecting a coating and completing our online quote request form.
Go to our coating applications page to learn more about where SilcoTek® coatings solve material problems, or check out our webinar on selecting the right coating for your application.

Have a question about our coatings? Contact our Technical Service Team. Or find us on LinkedIn.











/Pinhole%20and%20Silcolloy.png?width=587&name=Pinhole%20and%20Silcolloy.png)








